Comprehensive Guide to Food Drying Techniques for Enhanced Preservation
Maximize Food Shelf Life: Discover the Benefits of Sun Drying
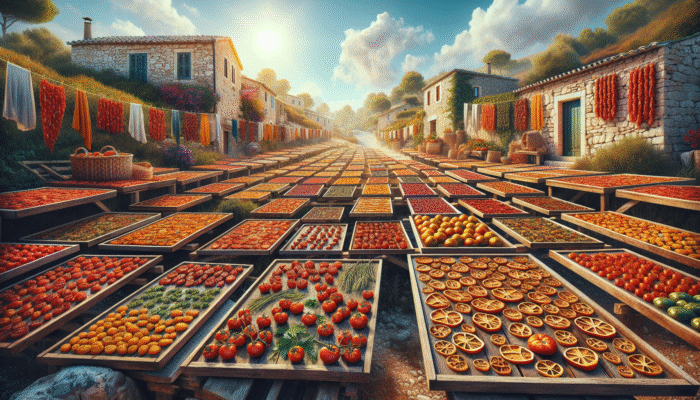
The traditional method of sun drying harnesses the natural energy of the sun to effectively remove moisture from a wide variety of foods, ensuring they remain preserved for extended periods while reducing the risk of spoilage. This technique is celebrated as one of the most straightforward and accessible food preservation methods, necessitating only minimal tools and equipment, making it suitable for an extensive array of food types such as fruits, vegetables, and herbs. Regions blessed with abundant sunshine, such as the Mediterranean and parts of Africa, have long adopted this practice. A classic illustration is the beloved Italian sun-dried tomatoes, which transform into succulent, flavor-packed ingredients that elevate countless culinary dishes.
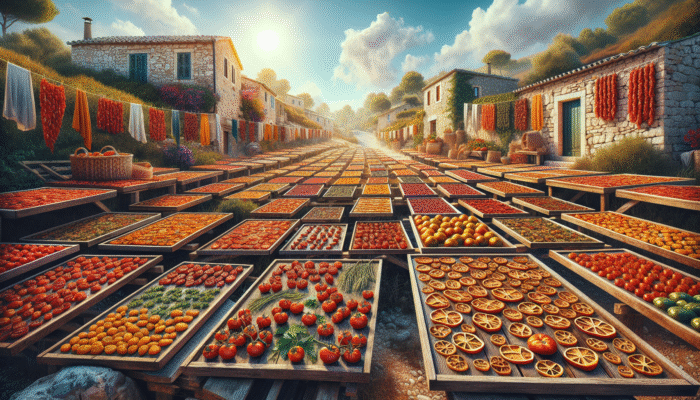

The sun drying process operates primarily on the principle of evaporation, where the heat from the sun encourages moisture to escape from the surface of the food. However, various factors such as ambient humidity and temperature play a significant role in the effectiveness of this technique. For instance, high humidity levels can impede the drying process, while clear, warm sunny days yield outstanding results. To achieve optimal drying, it is essential to cut the food into uniform slices and arrange it in a single layer on drying racks or trays. This method not only preserves the food but also intensifies its flavors, making sun-dried fruits sweeter and vegetables richer in taste.
Ensuring food safety during sun drying is of utmost importance; it is critical to dry the food thoroughly to prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms. Covering the food with a clean, breathable cloth during the drying process can effectively keep pests at bay while allowing for proper air circulation. This eco-friendly food preservation method operates entirely without electricity and produces minimal waste. In today’s eco-conscious society, where sustainable living is increasingly valued, sun drying is set to make a comeback as more individuals seek ways to enjoy seasonal produce throughout the year.
Effortless Air Drying: A Natural Approach to Food Preservation
Air drying is an uncomplicated and effective method for preserving food that utilizes natural air circulation to eliminate moisture, making it particularly advantageous for drying herbs and fruits. Unlike sun drying, it is less contingent on specific climatic conditions and can be practiced both indoors and outdoors, depending on the space available and environmental factors. This beloved technique is found in various cultures worldwide, including China, where herbs are commonly hung in bunches to dry, preserving their intense flavors and aromas.
The air drying process is straightforward and involves hanging or placing food items on racks to facilitate unobstructed airflow around them. This method is most effective in dry, warm conditions with low humidity levels. For example, herbs like basil and thyme can be harvested and hung upside down in a well-ventilated area to dry, resulting in concentrated flavors that enhance numerous culinary dishes. Maintaining a clean drying environment, free from insects and contaminants, is crucial, as proper sanitation is essential for successful food preservation.
Air drying not only helps preserve the flavors and nutrients of the food but also leads to a unique transformation in texture. Dried fruits, such as apples and apricots, become chewy and slightly caramelized, while herbs lose moisture and become more aromatic and intense in flavor. This technique stands out as one of the most cost-effective food preservation methods, requiring virtually no investment in specialized equipment. As global interest in home gardening and organic practices rises, air drying inspires individuals to maximize their harvests, minimize food waste, and elevate their culinary experiences.
Advanced Dehydration: Precision Techniques for Effective Food Preservation

Dehydration represents a modern approach within the realm of food preservation methods, utilizing controlled heat to extract moisture from food, significantly extending its shelf life. Unlike traditional drying methods, dehydration offers precise control over temperature and airflow, ensuring consistent and reliable results. This method is particularly favored for preserving meats and vegetables, establishing itself as a staple in both home kitchens and commercial food operations.
The dehydration process involves placing food in a specialized dehydrator or an oven set to a low temperature, allowing the heat to gradually evaporate moisture without cooking the food. For example, beef or turkey jerky undergoes dehydration, transforming into a protein-rich snack that can last for months without refrigeration. Similarly, dehydrated vegetables maintain much of their nutritional value and can be rehydrated in soups and stews, providing a convenient way to enjoy seasonal produce throughout the year.
One of the most significant advantages of dehydration is its ability to effectively retain the food’s flavor, color, and nutritional content. Unlike other preservation methods that may alter the original taste or texture, dehydration enhances these attributes, opening up creative culinary opportunities that go beyond mere storage. As health consciousness grows globally, dehydrated snacks made from fruits and vegetables have surged in popularity, offering a nutritious alternative to processed snacks.
With advancements in technology, home dehydrators have become increasingly affordable and user-friendly, enabling individuals to seamlessly integrate this method into their food preservation practices. The rising trend of healthy eating and the demand for alternatives to processed foods position dehydration as a sustainable solution that aligns with modern dietary preferences while simultaneously reducing food waste on a global scale.
Expert Canning Techniques for Sustainable Food Preservation
Water Bath Canning: An Enduring Method for Preserving High-Acid Foods
Water bath canning is a time-honored method that involves immersing jars filled with high-acid foods in boiling water to create a vacuum seal that effectively inhibits bacterial growth. This technique is ideal for preserving fruits, pickles, and jams that thrive in acidic environments. Originating centuries ago, water bath canning has been embraced globally, particularly in regions with rich agricultural traditions like North America and Europe.
The canning process begins with meticulously cleaning and sterilizing glass jars and lids, then filling them with prepared foods while leaving a small headspace at the top. Once sealed, the jars are submerged in boiling water for a designated duration, ensuring that the contents reach a sufficient temperature to eliminate bacteria and other microorganisms. This critical step is essential for maintaining food safety, as improper sealing could lead to spoilage or foodborne illnesses.
One remarkable aspect of water bath canning is its ability to beautifully preserve the natural flavors and colors of food. For instance, canning peaches locks in their radiant hue and sweet taste, delivering a burst of summer flavor during the colder winter months. Furthermore, this method allows for creative experimentation with seasonal produce, enabling home canners to explore unique recipes and flavor combinations.
However, it’s crucial to understand that water bath canning is only suitable for high-acid foods; low-acid foods like vegetables and meats necessitate pressure canning to ensure safety. As sustainable food practices gain traction worldwide, more individuals are rediscovering the joys of home canning, transforming their harvests into long-lasting culinary treasures. With a bit of practice and care, anyone can master this effective food preservation method, creating jars of deliciousness that bring joy to the table.
Pressure Canning: Essential Techniques for Safely Preserving Low-Acid Foods
Pressure canning is a crucial technique in food preservation, particularly for low-acid foods that require higher temperatures to eliminate harmful bacteria. This process employs a pressure canner, which elevates the boiling point of water, allowing food to be processed at temperatures exceeding 240°F (116°C). Consequently, pressure canning is vital for safely preserving vegetables, meats, and poultry, making it an essential skill for home canners and food enthusiasts alike.
The pressure canning process begins similarly to water bath canning, with the essential step of preparing and filling jars. However, once sealed, the jars are placed in the pressure canner, where they undergo a meticulous process of heating and pressurization. This method effectively destroys bacteria, yeasts, and molds that can thrive in low-acid environments, ensuring the safety and longevity of the preserved food.
In regions where agriculture flourishes, such as the Midwest United States, pressure canning has become a staple for families looking to stock their pantries with nutritious, homemade foods. By preserving summer’s bounty, from green beans to various meats, individuals can enjoy fresh flavors year-round, contributing to food security and minimizing waste.
While pressure canning offers numerous benefits, adhering to guidelines and using tested recipes is essential to mitigate safety risks. Each canning session provides an opportunity to engage in sustainable practices, maximizing local produce while reducing reliance on store-bought goods. In a world increasingly focused on self-sufficiency, mastering pressure canning yields delicious rewards and empowers individuals to take control of their food sources and promote a zero-waste lifestyle.
Atmospheric Steam Canning: Simplifying the Canning Process for Efficiency
A recent innovation in the canning world, atmospheric steam canning has emerged as an efficient method for preserving high-acid foods while simplifying the canning process. This technique utilizes steam instead of boiling water to process jars, creating a gentler environment that enhances flavor and texture. With its growing popularity worldwide, this method is rapidly gaining favor among home canners seeking convenience without compromising quality.
In atmospheric steam canning, jars are placed on a rack within a steam canner that heats water to generate steam, creating a vacuum seal as the jars are processed. This method requires less water than traditional water bath canning and significantly reduces processing times. For example, canning tomatoes or fruit preserves using steam can yield quicker, equally safe results, making it an attractive option for those with busy lifestyles.
The benefits of atmospheric steam canning extend beyond mere convenience. The steaming environment helps retain the food’s color, texture, and nutrients, resulting in preserved products that taste fresh and vibrant. As more individuals become aware of the advantages of preserving their food, steam canning presents a practical option that aligns with modern culinary needs.
One of the most appealing aspects of atmospheric steam canning is its ease of use. With clear instructions and minimal equipment required, it opens the world of canning to new enthusiasts who may have felt intimidated by traditional methods. As the trend toward homemade and locally sourced foods continues to rise, this technique stands out as an exciting addition to the growing list of food preservation methods, paving the way for flavorful creations that bring the essence of seasonal produce into the home kitchen.
Delving into Freezing Techniques for Effective Food Preservation

Blast Freezing: A Rapid Method for Superior Quality Preservation
Blast freezing has transformed the landscape of food preservation methods by introducing a rapid freezing technique that locks in the texture and nutritional value of food. This method involves quickly exposing food to extremely low temperatures (-30°F or -34°C), preventing the formation of large ice crystals that can damage cellular structures and degrade quality. This rapid process is especially beneficial for preserving fruits and vegetables, maintaining their vibrant colors and fresh flavors.
In commercial settings, blast freezing is widely utilized to preserve seafood, fruits, and ready-to-eat meals, enabling producers to offer high-quality products year-round. For instance, blast-frozen berries retain their plumpness and juicy flavor, making them ideal for smoothies, desserts, or breakfast bowls. This technique is not limited to industrial applications; home freezers equipped with quick-freeze settings can adopt this method to enhance food quality.
The advantages of blast freezing extend beyond flavor preservation, as it significantly reduces food waste. By freezing seasonal produce at its peak freshness, individuals can enjoy the benefits of homegrown or locally sourced foods throughout the year. This trend aligns with the increasing focus on sustainable living and minimizing carbon footprints, as frozen foods boast a longer shelf life and can be utilized as needed.
While blast freezing is an advanced technique, its principles can inspire home cooks to adopt freezing as a reliable food preservation method. By effectively mastering the art of freezing fruits, vegetables, and meals, individuals can create a well-stocked freezer that offers convenience and healthy options, making it easier to prepare nutritious meals on busy days.
Slow Freezing: A Timeless Approach to Food Preservation
Slow freezing is a more traditional approach to food preservation that occurs gradually at higher temperatures than blast freezing. This method is particularly suitable for meats and certain vegetables, allowing for a controlled freezing environment that effectively maintains quality and taste. While it may not achieve the rapid results of blast freezing, slow freezing possesses its own unique advantages within food preservation methods.
When employing slow freezing, food is typically stored in standard home freezers, where temperatures hover around 0°F (-18°C). This method allows food to freeze gradually, enhancing the texture of meats, resulting in a more tender final product when cooked. For instance, if packaged and stored properly, frozen chicken or beef can retain its original flavor and moisture content.
One of the key benefits of slow freezing is its accessibility; virtually anyone with a home freezer can implement this method. It provides a simple way to extend the shelf life of meats, fruits, and vegetables, allowing individuals to take advantage of bulk purchases and seasonal harvests. However, proper packaging is crucial to prevent freezer burn and maintain quality over time. Vacuum-sealing or tightly wrapping food in plastic can further enhance the preservation process.
Slow freezing encourages individuals to maximize their culinary resources as awareness of food waste issues grows. By learning to freeze leftovers, bulk purchases, or excess harvests, individuals can minimize waste while ensuring they always have delicious, home-cooked meals readily available. This sustainable approach to food preservation resonates with the global push for eco-friendly practices and responsible consumption.
Cryogenic Freezing: Cutting-Edge Preservation Techniques for Superior Quality
Cryogenic freezing is a state-of-the-art method of food preservation that employs liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide to achieve ultra-fast freezing rates. This technology is often utilized in commercial settings, particularly for delicate foods like seafood, fruits, and gourmet dishes, where maintaining quality is of utmost importance. The rapid freezing process prevents the formation of large ice crystals, ensuring that the food retains its original texture, taste, and nutritional value.
Cryogenic freezing operates at around -320°F (-196°C), creating an environment where food freezes almost instantaneously. This is especially beneficial for seafood, which can suffer from texture degradation if frozen too slowly. This method allows producers to offer high-quality seafood with optimal freshness, appealing to consumers looking for premium products.
While cryogenic freezing is generally associated with commercial applications, its principles can inspire home cooks to explore new food preservation techniques. Understanding the significance of quick freezing can motivate individuals to implement strategies such as portioning and freezing seafood immediately upon purchase, ensuring that flavors and nutrients are locked in from harvest.
As the culinary world embraces innovation, cryogenic freezing serves as a reminder of the evolving landscape of food preservation. The ongoing development of technology promises exciting possibilities for maintaining food integrity while extending its shelf life, paving the way for a future where freshness is accessible to all.
Individual Quick Freezing: Precision Preservation for Optimal Quality Maintenance
Individual Quick Freezing (IQF) is an exceptional technique that freezes individual food items separately, preventing them from clumping together. This method is particularly advantageous for fruits and seafood, as it effectively maintains quality and allows for easy portioning. IQF has become a staple in the food industry, presenting a convenient solution for consumers who value freshness and flexibility in their meals.
The IQF process involves rapidly freezing food at extremely low temperatures, ensuring that each piece freezes independently. This preserves the food’s texture and flavor while allowing for easy portioning during cooking or baking. For instance, frozen berries can be taken directly from the freezer and added to smoothies or baked goods without thawing, simplifying meal preparation and reducing waste.
One of IQF’s significant advantages is its ability to extend the shelf life of foods while preserving their nutritional quality. By freezing fruits and vegetables at their peak ripeness, consumers can enjoy the benefits of seasonal produce year-round. This approach aligns with sustainability and responsible consumption, enabling individuals to support local farmers while minimizing food waste.
As more people become aware of the advantages of IQF, it is likely to gain traction in home kitchens as well. Implementing similar techniques, such as freezing individual portions of meal prep items or using trays to freeze fruits and herbs separately, can help individuals create a well-stocked freezer that meets their culinary needs. By adopting IQF principles, anyone can take control of food preservation, ensuring freshness and quality are always within reach.
Exploring Fermentation Techniques for Food Preservation
Understanding Lactic Acid Fermentation: Enhancing Flavors through Preservation
Lactic acid fermentation is a fascinating and ancient food preservation method that converts sugars into lactic acid, effectively preserving food while enhancing its flavors. This technique is widely utilized across various cultures, from Korea’s iconic kimchi to Germany’s tangy sauerkraut, showcasing the diverse applications of fermentation. The process not only extends the shelf life of vegetables but also adds unique tastes and nutritional benefits.
At its core, lactic acid fermentation relies on beneficial bacteria, primarily Lactobacillus, which thrive in anaerobic conditions. When vegetables are submerged in a saltwater brine, these bacteria flourish, converting sugars in the food into lactic acid. This acid lowers the food’s pH, creating an inhospitable environment for harmful bacteria while promoting the growth of probiotics—beneficial microorganisms that offer numerous health benefits.
Lactic acid fermentation is versatile, extending beyond vegetables to include dairy products like yogurt and kefir. As the fermentation process unfolds, flavors develop complexity, while the probiotics contribute to gut health, making these foods not only delicious but also nutritious. The global trend toward health-conscious eating has sparked renewed interest in fermented foods, as people seek natural ways to elevate their diets.
Engaging in lactic acid fermentation at home can be a fulfilling endeavor. Simple recipes for pickles, kimchi, or yogurt allow individuals to explore this ancient technique, promoting self-sufficiency and sustainability. By incorporating lactic acid fermentation into their culinary repertoire, home cooks can create flavorful, healthful foods that connect them with culinary traditions worldwide.
Alcoholic Fermentation: Crafting Beverages through a Timeless Process
Alcoholic fermentation is a transformative process that converts sugars into alcohol, extensively employed in the production of beverages such as wine, beer, and spirits. This ancient practice dates back thousands of years and has roots in cultures across the globe. As one of the central food preservation methods, alcoholic fermentation not only creates delightful beverages but also extends the shelf life of fruits and grains.
Fermentation occurs when yeast, a microscopic fungus, consumes sugars and produces alcohol and carbon dioxide as byproducts. This natural process has given rise to a wide array of traditional beverages, from France’s rich red wines to Belgium’s golden ales. Each culture adds its unique twist to alcoholic fermentation, resulting in diverse flavors and styles that continually captivate consumers.
In addition to its cultural significance, alcoholic fermentation provides practical benefits for food preservation. The alcohol produced during fermentation acts as a natural preservative, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria and allowing for extended storage of beverages. For instance, mead, a fermented drink made from honey and water, has been enjoyed for centuries and can be stored for years, with its flavors evolving beautifully over time.
Home fermentation of alcoholic beverages has gained popularity recently, allowing individuals to explore the art and science behind brewing and winemaking. This provides an opportunity for creativity and experimentation while fostering a deeper connection to food and drink. Whether crafting a small batch of cider or experimenting with unique flavor combinations, individuals can take pride in their creations, celebrating the age-old tradition of alcoholic fermentation while enjoying delicious, homemade beverages.
Acetic Acid Fermentation: Producing Versatile Vinegar for Culinary Applications
Acetic acid fermentation is a critical process that produces vinegar, a versatile ingredient widely used for cooking and preserving foods. This technique relies on acetic acid bacteria to convert alcohol into acetic acid, yielding a sour flavor that enhances dishes and extends their shelf life. As one of the most recognized food preservation methods, acetic acid fermentation boasts deep historical roots, with vinegar production dating back thousands of years.
The fermentation process begins with converting sugars into alcohol, followed by introducing acetic acid bacteria. These microorganisms thrive in oxygen-rich environments, feeding on the alcohol and converting it into acetic acid. The result is a tangy, flavorful vinegar that can elevate countless dishes, from salad dressings to marinades. Varieties such as balsamic vinegar from Italy and apple cider vinegar from the United States exemplify the diverse options produced through this method.
Acetic acid fermentation not only enhances flavor but also serves as a powerful preservative. The acidity of vinegar prevents spoilage by creating an inhospitable environment for harmful microorganisms, making it an ideal solution for pickling vegetables and fruits. As the trend toward homemade pickles and preserves persists, acetic acid fermentation allows individuals to experiment with flavors and ingredients, transforming seasonal produce into long-lasting culinary delights.
Making vinegar at home can be a rewarding venture for those interested in exploring acetic acid fermentation. With simple ingredients and a bit of patience, anyone can create unique vinegar flavors, infusing creativity into their culinary endeavors. As this ancient technique gains renewed interest, it serves as a reminder of fermentation’s power as a sustainable and flavorful food preservation method.
Exploring Pickling Techniques for Flavor and Freshness Preservation
The Art of Vinegar Pickling: A Time-Honored Preservation Technique
Vinegar pickling is a cherished food preservation method that utilizes vinegar’s acidic properties to preserve and enhance the flavor of various vegetables and fruits. This technique has been practiced for centuries and has roots in diverse cultures worldwide. From tangy pickles to zesty relishes, vinegar pickling not only extends the shelf life of foods but also elevates their flavors, making it a staple in many kitchens.
The vinegar pickling process commences with preparing vegetables or fruits, which are submerged in a vinegar solution, often accompanied by spices, herbs, and salt. The acidity of the vinegar creates an inhospitable environment for harmful bacteria, ensuring food safety while allowing beneficial fermentation to occur. For instance, cucumbers transformed into classic dill pickles deliver a crisp, tangy delight that complements countless dishes.
One of vinegar pickling’s significant advantages is its versatility. Various types of vinegar—from white and apple cider to rice and balsamic—can be used to create an extensive range of flavors and profiles. Additionally, the infusion of spices and herbs allows for endless possibilities, catering to diverse culinary preferences. With the increasing demand for homemade and artisanal foods, vinegar pickling provides an accessible and rewarding avenue for food enthusiasts.
Beyond preservation, vinegar pickling offers numerous health benefits. Pickled foods are rich in probiotics, which can support gut health and digestion. The tangy, flavorful results of pickling also encourage individuals to incorporate more vegetables into their diets, aligning with the trend of healthy eating. As a sustainable practice, vinegar pickling reduces food waste and cultivates a deeper connection to seasonal produce, making it a cherished method in modern kitchens.
The Joy of Brine Pickling: A Flavorful Preservation Technique
Brine pickling is a delightful food preservation method that involves soaking vegetables in a saltwater solution to ferment and preserve them while intensifying their flavors. This traditional technique has been utilized for centuries, with variations found in cultures across the globe. Brine pickling produces a variety of delicious options, from tangy sauerkraut to flavorful pickles, making it a staple in many households.
The brining process begins with creating a saltwater solution, where the concentration of salt plays a crucial role in both preservation and flavor development. As the vegetables soak in the brine, the salt draws out moisture, creating a favorable environment for beneficial bacteria to thrive. These bacteria ferment the sugars in the vegetables, producing lactic acid and contributing to the characteristic sour flavor of fermented pickles.
Brine pickling not only preserves the food but also enhances its nutritional profile. The fermentation process increases the bioavailability of certain nutrients, making them easier for the body to absorb. Additionally, probiotics promote gut health, further contributing to the appeal of brined foods in modern diets.
This method offers various creative possibilities, allowing individuals to experiment with different vegetables, spices, and seasonings. From classic dill pickles to more adventurous options like pickled carrots or beets, brine pickling opens the door to culinary exploration. As people increasingly seek to connect with their food and reduce waste, brine pickling provides an accessible, home-based solution for preserving seasonal produce while adding exciting flavors to meals.
Dry Salting: An Ancient Technique for Effective Food Preservation
Dry salting is an ancient food preservation method that applies salt directly to draw out moisture, effectively preserving meats and fish. This technique has been utilized across various cultures and regions, significantly aiding food storage long before refrigeration became prevalent. Dry salting extends shelf life and enhances flavors, making it a revered practice in culinary traditions worldwide.
The dry salting process is relatively straightforward: salt is rubbed directly onto the surface of the food, creating an environment where moisture is drawn out, inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria. For instance, dry-cured meats such as prosciutto or salami are made using this method, resulting in intensely flavored products that develop rich, complex tastes over time. The salting process also contributes to these cured meats’ unique texture and aroma, making them sought after by both chefs and home cooks alike.
One of the key benefits of dry salting is its ability to enhance flavor while preserving the food. The salt penetrates the meat or fish, infusing it with seasoning and preventing spoilage. As a result, individuals can enjoy high-quality, flavorful products without chemical preservatives. This aligns with the growing clean eating trend, where consumers seek natural alternatives to processed foods.
While dry salting is often associated with meat, it can also enhance the flavors of certain fruits and vegetables, such as eggplant or cucumbers. This versatility allows home cooks to explore new avenues for preservation and flavor enhancement. As the desire for sustainable practices grows, dry salting serves as a reminder of the age-old techniques that continue to bring joy to the table while connecting us to our culinary heritage.
Exploring Smoking Techniques for Enhanced Food Preservation
Cold Smoking: A Unique Technique for Flavor Infusion
Cold smoking is an intriguing food preservation method that enriches the flavor of foods without cooking them. This technique involves exposing food to smoke from burning wood at low temperatures, typically below 85°F (29°C), allowing the smoke to permeate the food while preserving its original texture. With roots in various cultures worldwide, cold smoking has become a cherished practice for enhancing meats, cheeses, and even vegetables.
The cold smoking process begins with selecting the appropriate wood, as different woods can significantly impact the flavor profile. For instance, hickory and mesquite provide bold flavors, while fruitwoods like cherry or apple lend a milder sweetness. The food is then placed in a smoker or a cold smoking chamber and exposed to the smoke for an extended period, allowing the flavors to develop gradually.
One of the key advantages of cold smoking is its ability to preserve food while imparting unique flavors. For example, cold-smoked salmon or cheese retains its original taste and texture while gaining a smokiness that elevates culinary creations. This method enhances flavor and helps prolong shelf life, as the smoke acts as a natural preservative.
As the trend toward artisanal and homemade foods grows, many individuals are exploring cold smoking to infuse creativity into their cooking. Home cooks can create flavorful smoked products with simple equipment and experimentation, from meats to vegetables. Cold smoking serves as a delightful reminder of the art of preservation, merging flavor and tradition in a harmonious culinary experience.
Hot Smoking: A Dynamic Technique for Cooking and Preservation
Hot smoking combines the processes of cooking and smoking, resulting in a dynamic food preservation method that enhances flavors while preserving food. This technique involves exposing food to smoke at higher temperatures, typically ranging from 165°F to 250°F (74°C to 121°C), allowing the food to cook while absorbing rich, smoky flavors. Popular in various cultures, hot smoking has become a staple for meats, fish, and vegetables, offering a unique culinary experience.
The hot smoking process begins with selecting the desired wood and preparing the food for smoking. Marinating or seasoning the food can enhance flavor, while the choice of wood influences the final taste. As the food is placed in the smoker, it cooks while enveloped in smoke, resulting in tender, flavorful dishes. For example, hot-smoked brisket or ribs develop a beautiful crust while remaining juicy and infused with the essence of smoke.
One of the primary benefits of hot smoking is its ability to preserve food naturally while imparting bold flavors. The combination of cooking and smoking extends the shelf life of meats while creating tantalizing dishes perfect for gatherings and home meals. As the trend toward outdoor cooking and smoking continues to rise, many individuals are discovering the joys of hot smoking as a way to elevate their culinary repertoire.
Additionally, hot smoking allows for creativity in the kitchen, as various types of food can be experimented with. From smoked chicken wings to vegetables, the possibilities are endless. By incorporating hot smoking into their cooking practices, individuals can enjoy delicious, home-cooked meals that celebrate flavors and bring loved ones together around the table.
Liquid Smoke: Convenient Flavor Enhancement for Home Cooking
Liquid smoke is an intriguing product that encapsulates the essence of traditional smoking in a convenient form. This concentrated smoke flavor is created by condensing the smoke from burning wood chips, allowing home cooks and chefs to infuse their dishes with a robust smoky aroma without elaborate smoking equipment.
Liquid smoke is simple and versatile. It can be added to marinades, sauces, or directly to foods, providing an immediate smoky flavor that enhances everything from grilled meats to soups. For instance, a few drops of liquid smoke can transform a simple barbecue sauce into a rich, smoky concoction that elevates grilled ribs or burgers. With its concentrated form, liquid smoke offers a quick and efficient way to achieve that coveted smoked flavor without the lengthy process of traditional smoking.
One key advantage of using liquid smoke is its accessibility. Individuals who may lack the space or equipment for traditional smoking can still enjoy the benefits of smoky flavors in their cooking. This convenience has made liquid smoke a popular choice for home cooks and food enthusiasts looking to add depth and complexity to their dishes.
While liquid smoke is a convenient alternative, it is essential to use it judiciously, as its concentrated nature can overpower dishes if used excessively. By experimenting with different recipes and finding the right balance, individuals can harness the power of liquid smoke to create flavorful, smoky creations that delight the palate. As culinary trends evolve, liquid smoke serves as a reminder of the innovative possibilities within food preservation methods.
Understanding Curing Techniques for Preserving Meats
Dry Curing: A Time-Tested Method for Flavor Preservation
Dry curing is a traditional food preservation method that employs salt and sometimes sugar to draw out moisture and enhance the flavors of meats, particularly pork. This ancient technique has been practiced for centuries, yielding iconic products such as prosciutto, salami, and bacon. The process not only preserves the meat but intensifies its flavor, resulting in rich, complex tastes celebrated in culinary traditions worldwide.
The dry curing process begins with applying a mixture of salt and spices directly to the surface of the meat. The salt draws out moisture, creating an environment where bacteria cannot thrive while infusing the meat with flavor. As curing progresses, the meat loses weight and develops a firm texture characteristic of cured products. For instance, dry-cured ham showcases the transformative effects of this method, resulting in a savory, melt-in-your-mouth delicacy.
One of the key benefits of dry curing is its ability to enhance the meat’s natural flavors while extending its shelf life. The salt acts as a preservative and intensifies the taste, making cured meats a sought-after ingredient in numerous dishes. Additionally, dry curing offers a sustainable way to preserve meat, allowing individuals to utilize whole cuts and reduce waste.
As the trend toward artisanal and homemade foods gains momentum, many individuals are rediscovering the art of dry curing at home. While the process requires patience and attention to detail, the results are undeniably rewarding, providing a connection to culinary traditions and the satisfaction of creating high-quality products. By mastering dry curing techniques, individuals can take pride in their craft while enjoying the delicious fruits of their labor.
Wet Curing: Infusing Flavor and Moisture into Meats
Wet curing, also known as brining, is a flavorful food preservation method that involves soaking meat in water, salt, and often sugar and spices. This technique has been employed for centuries to enhance the flavors, tenderness, and shelf life of various meats, making it a popular choice for home cooks and professional chefs alike. Wet curing offers a unique approach to preserving meat while imparting delicious flavors that elevate dishes.
The wet curing process begins with preparing the brine solution, where the concentration of salt and other ingredients is crucial for success. The meat is submerged in the brine and left to soak for a specified period, allowing the salt to penetrate the meat and enhance its flavor. For example, wet-cured turkey or ham can yield juicy and flavorful products, perfect for festive gatherings or special occasions.
One significant advantage of wet curing is its ability to infuse meats with moisture, leading to tender and succulent results. The brine preserves the meat while enhancing its natural flavors, making it a standout ingredient in various dishes. Additionally, wet curing offers a sustainable approach to meat preservation, allowing individuals to utilize cuts that might otherwise go to waste.
As the trend toward homemade and artisanal foods continues, wet curing allows individuals to explore new flavors and techniques. By experimenting with different brine recipes and seasonings, home cooks can create unique cured meats that reflect their culinary preferences. This connection to the art of preservation fosters a deeper appreciation for food and encourages sustainable practices in the kitchen.
Combination Curing: Merging Techniques for Optimal Preservation
Combination curing is a versatile food preservation method that merges both dry and wet curing techniques to achieve optimal flavor and preservation in meats. This innovative approach allows for a more nuanced flavor profile and unique texture, making it particularly popular among artisanal producers and home cooks aiming to elevate their charcuterie skills.
The combination curing process typically begins with applying a dry cure to the meat, followed by a soak in a brine solution. This dual approach allows the salt and spices to penetrate the meat deeply while enhancing moisture retention. Products like pancetta and smoked sausages often utilize this method, resulting in complex flavors and textures cherished in culinary traditions worldwide.
One of the primary benefits of combination curing is its ability to balance flavor and preservation. The initial dry cure helps draw out moisture, while the subsequent brining process infuses the meat with additional flavor and juiciness. This method allows for greater creativity in the kitchen, as home cooks can experiment with various flavor combinations, from herbs and spices to unique marinades.
As interest in artisanal and homemade foods grows, combination curing provides an exciting opportunity for individuals looking to master the art of preservation. By exploring the intricacies of this technique, home cooks can create high-quality cured meats that reflect their culinary preferences while connecting with traditional practices. This method reinforces the importance of sustainability and celebrates the rich heritage of food preservation.
Equilibrium Curing: Precision in Meat Preservation
Equilibrium curing is an advanced food preservation method that utilizes precise amounts of salt and other ingredients to cure meats consistently. This technique is gaining traction among charcuterie enthusiasts and professional chefs, allowing for greater control over flavor, texture, and preservation. By balancing the ratio of salt to meat carefully, equilibrium curing results in a product that is both flavorful and safe for consumption.
In equilibrium curing, the amount of salt used is calculated based on the weight of the meat, ensuring that the cure penetrates evenly. This method enables the meat to retain moisture while preventing spoilage, producing a tender and flavorful final product. For example, equilibrium-cured duck breast can be transformed into a delicacy rich in flavor and perfect for various applications, from salads to charcuterie boards.
One of the key advantages of equilibrium curing is its precision. This method allows individuals to create consistently high-quality products, reducing the risk of over-curing or under-curing. Additionally, the scientific approach to curing aligns with the growing trend of precision cooking, where measurements and data play a crucial role in culinary success.
As the interest in sustainable and artisanal foods continues to rise, equilibrium curing presents an opportunity for home cooks to explore new techniques and elevate their charcuterie skills. By mastering this method, individuals can create unique cured meats that showcase their culinary prowess while engaging with traditional practices. This connection to the art of preservation enhances our understanding of food and celebrates the flavors and heritage that define our culinary landscape.
Fermentation Curing: Harnessing Bacteria for Distinctive Flavors
Fermentation curing is a captivating food preservation method that employs beneficial bacteria to enhance flavor and preserve meats. This technique is commonly utilized in producing cured sausage products such as salami and pepperoni, where the fermentation process plays a crucial role in developing complex flavors and ensuring food safety. With roots in various cultures, fermentation curing reflects the rich culinary traditions of meat preservation.
The fermentation curing process begins by introducing specific bacterial cultures into the meat mixture, often alongside spices and seasonings. These bacteria thrive in anaerobic environments, converting sugars into lactic acid while producing distinctive flavors. The result is a tangy, flavorful cured meat that is not only delicious but also safe for consumption, as the acidic environment helps inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria.
One of the key advantages of fermentation curing is its ability to create unique flavor profiles that stand out in the culinary landscape. The complex flavors developed during fermentation contribute to the distinctive taste of products like traditional Italian salami or Spanish chorizo, making them cherished ingredients in various dishes. Additionally, fermentation curing aligns with the trend of health-conscious eating, as these products offer beneficial probiotics and enhance gut health.
As interest in artisanal and homemade foods continues to rise, fermentation curing presents an exciting opportunity for individuals to explore the art of charcuterie. With a few simple ingredients and patience, home cooks can experiment with fermentation techniques, creating unique cured meats that reflect their culinary preferences. This connection to the art of preservation fosters a deeper appreciation for food and celebrates the rich heritage that informs our culinary choices.
Frequently Asked Questions About Effective Food Preservation Methods
What are food preservation methods?
Food preservation methods encompass various techniques employed to extend the shelf life of food, prevent spoilage, and maintain quality. These methods include drying, canning, freezing, fermentation, pickling, smoking, and curing.
How does drying preserve food?
Drying preserves food by eliminating moisture, which inhibits the growth of bacteria, yeasts, and molds. Techniques such as sun drying, air drying, and dehydration effectively concentrate flavors and enhance food longevity.
What distinguishes water bath canning from pressure canning?
Water bath canning is suited for high-acid foods like fruits and jams. In contrast, pressure canning is essential for low-acid foods such as vegetables and meats to ensure safety and prevent bacterial growth.
How does freezing impact food quality?
Freezing preserves food quality by halting the growth of bacteria and slowing down enzymatic reactions. Methods such as blast freezing and individual quick freezing help retain texture, flavor, and nutritional value.
What are the benefits of fermentation?
Fermentation enhances food flavor, extends shelf life, and increases nutritional benefits by introducing probiotics. It serves as a natural preservation method used in products like yogurt, sauerkraut, and fermented beverages.
Can pickling be performed at home?
Yes, vinegar or brine solutions can easily be utilized for pickling at home. This method enables individuals to preserve and flavor vegetables and fruits, making it a popular culinary practice.
What role does salt play in curing?
Salt plays a pivotal role in curing by drawing out moisture, inhibiting bacterial growth, and enhancing the flavor of meats. Techniques such as dry and wet curing utilize salt for effective preservation.
How does smoking preserve food?
Smoking preserves food by exposing it to smoke from burning wood, which enriches flavor and creates an environment that inhibits spoilage. Cold smoking and hot smoking are popular methods that enhance taste.
What are some creative uses for liquid smoke?
Liquid smoke can be added to marinades, sauces, or directly to foods to impart a smoky flavor without traditional smoking. It’s a convenient way to enhance dishes like grilled meats and soups.
Is it safe to preserve food at home?
Following proper techniques and guidelines can ensure safe food preservation at home. Utilizing tested recipes and maintaining cleanliness are crucial to preventing spoilage or foodborne illnesses.
Join us on our journey on X!
The post Food Preservation Methods: A Comprehensive Guide appeared first on Survival Bite.
The Article Food Preservation Methods: Essential Techniques Explained Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com