Master the Art of Selecting the Ideal Milk for Homemade Cheese Creation
Exploring Varieties of Milk for Optimal Cheese Crafting
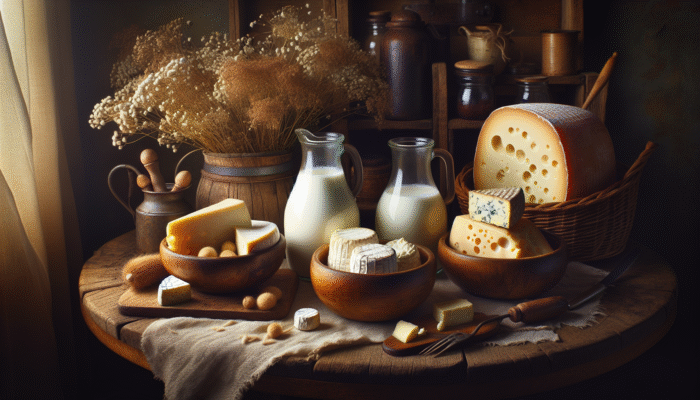

Choosing the perfect type of milk is essential for your cheese-making</b journey, as it serves as the backbone of your final cheese product. Different types of milk—such as whole, skim, and raw milk—offer distinctive characteristics that can significantly influence the flavor and texture of your cheese. Whole milk is frequently recommended for beginners, as its rich and creamy consistency provides an excellent base for a variety of cheese types. In contrast, skim milk tends to yield lighter cheeses that may lack the richness of their whole milk counterparts. On the other hand, raw milk, when obtained from reliable sources, can impart exceptional flavor and complexity to your cheese-making process; however, it requires a comprehensive understanding of food safety practices to ensure its proper handling. Your milk selection is not merely a choice; it profoundly shapes the essence of your cheese and can greatly impact your culinary achievements.
When evaluating your options, it is crucial to consider the availability of local sources. If you have the chance to obtain fresh raw milk from a nearby dairy farm, it could be an exciting avenue to explore, as the flavors obtained from freshly sourced milk often surpass those of mass-produced alternatives. Supporting local farmers not only enriches your cheese-making experience but also fosters sustainability within your community. If raw milk is unavailable, opting for organic whole milk from your local grocery store is a dependable alternative that still offers satisfying and flavorful outcomes.
Grasping the Importance of Milk Pasteurization in Cheese-Making
Understanding the function of pasteurization is essential for anyone embarking on their cheese-making adventure. This vital process involves heating milk to destroy harmful bacteria, ensuring its safety for consumption. While pasteurization provides a protective layer, it can also alter the flavor profile and texture of your cheese. Many expert cheesemakers champion the robust flavors that raw milk cheeses can achieve, which pasteurized varieties may lack. The decision between raw and pasteurized milk ultimately hinges on personal taste preferences and food safety concerns, making it a critical element in your cheese-making journey.
If you choose to delve into the world of raw milk cheese, it’s vital to adhere to local regulations and source your milk from reputable farms to mitigate the risks associated with unpasteurized products. Conversely, if you select pasteurized milk, you need not worry; a variety of delectable cheese types can still be produced in your kitchen. Embrace the medium you opt for and refine your techniques accordingly for the best results.
Finding Trustworthy Milk Sources for Successful Cheese Production
Discovering high-quality milk begins with knowing where to search. Regular visits to local farmers’ markets, joining co-ops, and exploring health food stores can lead you to premium dairy products. When selecting your milk, it’s essential to ask about its origin: Is it organic? What feeding practices are utilized for the cows? The answers to these inquiries can greatly influence the flavor and overall quality of your cheese, paving the way for a rewarding cheese-making experience.
Consider engaging with local food groups or joining online communities centered around cheese-making. These platforms can provide invaluable recommendations for trustworthy suppliers and create a shared knowledge base, making your cheese-making journey more enjoyable and fulfilling. Remember, the milk you choose is not just an ingredient; it is a crucial element that can elevate your homemade cheese to gourmet status.
Understanding Milk Fat Content and Its Impact on Cheese Creation
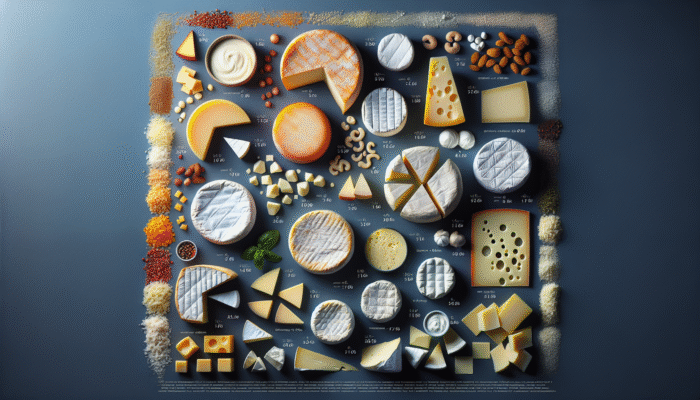

The fat content of milk plays a pivotal role in cheese production, significantly affecting the final characteristics of the product. Higher fat levels typically yield creamier and more indulgent cheeses, while lower-fat options may create lighter, less rich textures. If your goal is to produce a luxurious cheddar or decadent brie, selecting whole or even higher-fat milk is crucial. Conversely, those interested in crafting more delicate cheeses, like mozzarella, might find it beneficial to experiment with various fat levels for unique results and textures.
By understanding the science behind fat content and its correlation with texture, you can skillfully tailor your recipes. For example, adding cream to skim milk can create a delightful balance, allowing you to enjoy the best of both worlds. Delving into this aspect of cheese-making reveals an abundance of possibilities waiting to be uncovered, empowering you to produce cheeses tailored to your taste preferences and culinary aspirations.
Key Practices for Milk Storage and Handling in Cheese-Making
The importance of proper milk storage and handling cannot be overstated in the cheese-making process. To maintain its integrity, milk should always be refrigerated and consumed before its expiration date. Strive to use fresh milk for cheese-making; the fresher the milk, the more flavorful your cheese will be. If you purchase milk in bulk, consider freezing some to extend its shelf life, but be mindful that this may slightly alter its texture.
Before embarking on your cheese-making adventure, ensure that all your equipment is thoroughly sterilized and that you’re working in a pristine environment. Contamination can spoil your entire batch, leading to disappointing results. By prioritizing cleanliness and proper handling techniques, you position yourself for cheese-making success, ensuring that every bite is as delicious as you envisioned.
Essential Equipment and Ingredients for Home Cheese-Making
Must-Have Cheese-Making Tools for Aspiring Cheesemakers
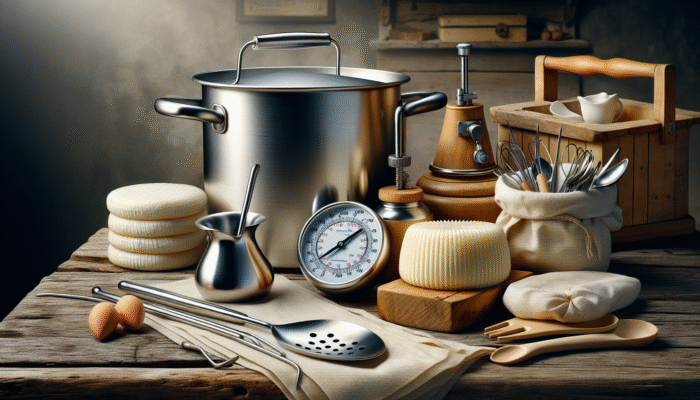

Embarking on your cheese-making journey necessitates having the right tools at your disposal. Essential equipment includes a large stainless steel pot, a dependable thermometer, fine cheesecloth, and a slotted spoon. A quality cheese mould enhances both the shape and presentation of your cheese, while an accurate dairy thermometer ensures that your milk reaches the optimal temperature for curdling. Investing in high-quality tools not only streamlines your process but also significantly enhances the quality of your final product.
For dedicated cheese-makers, adding a cheese press to your toolkit is worthwhile. This device applies consistent pressure during the draining process, resulting in firmer and more refined cheese. Additionally, utilizing a cheese mat for aging your creations can remarkably improve the final product. By thoughtfully selecting your tools, you are not merely preparing to make cheese; you are setting the stage for a delightful culinary adventure.
The Integral Role of Cultures and Rennet in Cheese Production
Cultures and rennet are indispensable components in the cheese-making process, crucial for curdling the milk and developing the desired flavor profile. Cultures consist of specific bacterial strains that ferment lactose into lactic acid, which is vital for flavor enhancement and the texture of cheese. Each cheese variety requires particular cultures, so understanding their roles will greatly enhance your creativity throughout the cheese-making journey.
Rennet is the enzyme that facilitates milk coagulation, leading to the formation of curds and whey. While traditional rennet is derived from animal sources, vegetarian alternatives are also available, accommodating diverse dietary preferences. Experimenting with various cultures and rennets can yield exciting variations in your cheese, allowing you to explore new flavors and textures that delight the senses and elevate your culinary creations.
Creative Ingredients to Enhance Your Cheese’s Flavor Profile
While milk, cultures, and rennet form the foundation of your cheese, don’t hesitate to be inventive with additional ingredients that can elevate your culinary creation. Ingredients such as herbs, spices, and even infused oils can transform a simple cheese into a gourmet delight. Consider incorporating garlic and basil for a fresh twist or experimenting with smoked paprika for a robust flavor profile that excites the palate and enhances your cheese’s complexity.
For those who enjoy a touch of sweetness, adding honey or fruit to your cheese can yield delightful results. Imagine creating a creamy goat cheese infused with figs or a tangy cheddar enhanced with jalapeños. The realm of cheese-making is vast and varied; let your imagination run wild and see where your creativity takes you as you explore unique flavor combinations that tantalize the taste buds.
Comprehensive Guide to the Home Cheese-Making Process
Steps to Prepare Milk Effectively for Cheese Production
Preparation is a critical stage in cheese-making that can significantly influence the final outcome. Begin by pouring your chosen milk into a large, heavy-bottomed pot, ensuring even heating. Gradually heat the milk over medium heat, using a thermometer to monitor the temperature accurately. Your objective is to reach the specific temperature required for the type of cheese you are producing, which generally ranges between 85°F to 190°F (approximately 29°C to 88°C).
Once you’ve reached the desired temperature, gently stir the milk to promote even heating throughout. At this juncture, it’s also beneficial to incorporate any additional ingredients, such as salt or herbs, before introducing your cultures. This moment marks the beginning of the transformation; the correct temperatures and cultures will lay the foundation for curd formation, initiating the fascinating cheese-making process.
Techniques for Curdling and Cutting Milk in Cheese Production
With your milk properly prepared, it’s time to curdle it. Introduce the rennet according to the package instructions, stirring gently for about 30 seconds before stopping the stirring to allow the milk to sit undisturbed for 5-10 minutes. During this crucial period, the curds will begin to form, and you will notice the separation of whey from the curds, indicating progress in your cheese-making process.
Once the desired curd formation is achieved, the next step is to cut the curds into manageable pieces. Using a long knife or a curd cutter, slice the curds into uniform sizes; this uniformity is vital for proper drainage. The size of the curds can significantly affect the texture of your finished cheese, so take care to cut them consistently. This cutting process also aids in releasing more whey, contributing to the overall firmness and quality of your cheese.
Draining and Pressing Curds for Ideal Cheese Texture
After cutting your curds, the next step is to drain them effectively. Transfer the curds into a cheesecloth-lined colander, allowing the whey to drain away. The duration of this step can fluctuate, taking anywhere from 15 minutes to several hours, depending on the type of cheese you’re creating. If you’re making a firmer cheese, consider applying gentle pressure to the curds while they drain to expel more whey efficiently and enhance the final texture.
For many cheese varieties, pressing the curds is a vital concluding step. Move the curds into your cheese mould and apply weight to achieve a firmer texture. The pressing process can range from a few hours to a full day, depending on the type of cheese you are pursuing. With patience and care, you will create a quality cheese that boasts rich flavor and satisfying texture, showcasing your efforts in the kitchen.
Discovering the Wide Array of Cheeses You Can Craft at Home
Effortlessly Create Soft Cheeses at Home
Soft cheeses, such as ricotta and feta, are among the simplest varieties to produce at home. Ricotta, known for its creamy texture and mild flavor, can be made using just milk, an acid (like lemon juice or vinegar), and a pinch of salt. Start by heating your milk, adding the acid, and allowing the curds to form. After draining, you’ll have a fresh, delightful cheese that’s perfect for spreads or versatile culinary applications.
Conversely, feta requires an additional step. After the curdling and draining process, the curds are crumbled and immersed in a brine solution. This method intensifies the flavor and extends the cheese’s shelf life, allowing you to enjoy its unique characteristics for a longer duration. The versatility of soft cheeses is a beautiful aspect; savor them fresh or incorporate them into salads, pastas, or even sweet desserts for an exciting culinary twist.
Mastering Hard Cheeses for the Dedicated Cheese Maker
For those determined to master the art of hard cheeses like cheddar or parmesan, the process becomes more intricate and rewarding. Starting with high-quality milk, the initial steps closely resemble those of soft cheese-making, but they involve more advanced techniques, including a longer aging period. Cheddar, for example, necessitates cutting the curds into smaller pieces and heating them more thoroughly to develop its signature sharp flavor.
Aging is the defining factor for hard cheeses. After pressing the curds into blocks, they should be carefully wrapped in cheese paper and stored in an environment with controlled temperature and humidity. The aging process can last from a few months for a mild cheddar to over a year for a mature parmesan. Monitoring your cheese during this period is crucial for developing the desired flavor profile and texture, making this phase a rewarding aspect of cheese-making.
Delving into Flavored Cheeses for Culinary Creativity
Enhance your cheese-making skills by exploring the world of flavored cheeses. The addition of herbs, spices, and even fruits can yield unique flavor combinations that excite the palate. Consider infusing your mozzarella with fresh basil and sun-dried tomatoes or blending soft goat cheese with honey and walnuts for a delectable spread that impresses both guests and family alike.
Flavoring your cheese can involve various techniques, such as marinating or smoking. By immersing your cheese in olive oil with garlic and rosemary or cold-smoking your cheddar, you can impart intricate flavors that make your homemade cheese truly distinctive. The possibilities for creating flavored cheeses are limited only by your imagination, so don’t hesitate to experiment with new combinations that inspire your culinary creativity.
Proven Strategies for Aging and Storing Cheese Effectively at Home
Perfecting Cheese Aging Techniques for Enhanced Flavor Development
The aging process is where the true artistry unfolds, transforming fresh curds into flavorful masterpieces. Different cheeses require various aging techniques, influenced by factors such as moisture content and desired texture. Generally, hard cheeses benefit from extended aging periods, while soft cheeses are best enjoyed fresh or within a few weeks for optimal flavor.
Control is essential during the aging stage. Maintaining consistent temperature and humidity levels is vital to encourage proper maturation. Many cheesemakers utilize aging caves or dedicated cheese fridges to create the ideal environment for their creations. As your cheese ages, it will develop distinct flavors, aromas, and textures, making this a dynamic and fulfilling journey for any cheese enthusiast.
Optimal Storage Conditions for Long-Lasting Cheese Quality
Proper storage is critical for preserving the quality of your cheese. Hard cheeses should be wrapped in parchment paper or cheese paper, allowing them to breathe while preventing moisture accumulation. In contrast, soft cheeses require airtight containers to avoid drying out, especially during storage. Always keep your cheese refrigerated, but allow it to come to room temperature before serving to enhance its flavor and texture, showcasing your hard work and dedication.
For extended storage, consider vacuum-sealing your cheese. This technique can significantly prolong its shelf life, keeping it fresh and flavorful for several months. However, it’s essential to regularly inspect stored cheese for signs of spoilage, such as unusual odors or mold, to ensure its quality remains intact and safe for consumption.
Monitoring Cheese Maturation for Optimal Flavor and Texture
Keeping a close eye on your cheese as it matures is crucial for achieving the best results. Regular checks will enable you to assess the texture, aroma, and flavor development of your cheese. Look for indicators that suggest your cheese is aging correctly, such as a firm rind or changes in color that signify the maturation process is progressing as it should.
As your cheese matures, tasting small samples can provide insight into its progress. This not only informs you about flavor development but also allows you to adjust future batches based on your personal preferences. The journey through maturation is not merely a waiting game; it’s an engaging experience with your cheese, ensuring it reaches its peak potential, resulting in a product you can take pride in.
Tackling Common Aging Issues with Effective Solutions
Every cheesemaker may face challenges throughout the aging process. Common problems include excessive moisture, unwanted mold, or off-flavors that can detract from your final product. If you find that your cheese is too wet, consider increasing airflow in your aging environment or adjusting humidity levels to facilitate proper drying. For unwanted mold, trim it away carefully, but remain vigilant, as certain molds can pose health risks if consumed.
Off-flavors can arise from various sources, including the quality of milk used or environmental factors. Maintaining cleanliness throughout the cheese-making process is essential to prevent contamination, which can lead to undesirable flavors. If persistent issues arise, revisiting the quality of your milk or adjusting your aging conditions can help identify potential solutions. Embrace these challenges as opportunities to refine your craft, ultimately leading to superior cheese in the long run.
Effective Troubleshooting Techniques for Common Cheese-Making Problems
Addressing Unwanted Textures in Your Cheese Creations
Texture is a defining characteristic of cheese, and encountering undesirable textures can be disheartening. If your cheese turns out grainy or overly crumbly, it may result from excessive heat during curd formation or cutting the curds too small. To prevent these issues, be vigilant about monitoring temperatures throughout the process and ensuring uniform curd sizes during cutting.
If you find that your cheese is too dry after aging, consider adjusting your pressing technique. This may involve reducing the pressure applied during the pressing stage or closely monitoring moisture levels during aging. Experimenting with these variables can lead to significant improvements in the consistency and texture of your cheese, enhancing the overall quality of your homemade creations.
Resolving Off-Flavors in Your Homemade Cheese
Off-flavors can pose a considerable setback in cheese-making. If you detect sour or rancid flavors in your cheese, this may indicate bacterial contamination or the use of low-quality milk. Ensuring that your equipment is clean and that you’re using fresh, high-quality ingredients is crucial for preventing these undesirable tastes from occurring.
Should you experience persistent off-flavors, consider experimenting with different cultures or adjusting your fermentation times. Sometimes, subtle changes in your method can lead to remarkable improvements in flavor. Stay open to constructive feedback and be willing to adapt; this flexibility is an integral part of the learning journey in cheese-making and can lead to delightful discoveries.
Preventing Contamination for Safe and Successful Cheese-Making
Maintaining a contamination-free environment is essential for both the safety and quality of your cheese. Always begin with sterilized equipment and ensure that you’re working in a clean space. Regularly wash your hands and avoid cross-contamination by separating raw and cooked ingredients to safeguard your process and ensure the integrity of your cheese.
Moreover, monitor your cheese during the aging phase. If you observe unwanted mold or unusual odors, take immediate action to address these issues to prevent spoilage. Familiarizing yourself with common risks and implementing diligent practices will protect your cheese-making efforts, ensuring that every batch is not only delicious but also safe for consumption.
Frequently Asked Questions About Home Cheese-Making
Which type of milk is optimal for cheese-making?
Whole milk is often recommended for beginners due to its rich flavor and creamy texture. Additionally, raw milk can offer even greater complexity, but it’s essential to ensure that it’s sourced safely from reputable suppliers to avoid health risks.
Is store-bought milk suitable for cheese-making?
Absolutely! Store-bought whole milk is an excellent choice for making cheese, particularly if raw milk isn’t available. If possible, opt for organic varieties to achieve the best outcomes in flavor and quality.
How long does the cheese-making process take at home?
The timeframe varies based on the type of cheese being produced. Soft cheeses can be ready in just a few hours, while hard cheeses may require months to age properly and develop their full flavor potential.
What should I do if my cheese fails to curdle?
If your cheese isn’t curdling, check the freshness of your rennet, verify that the temperatures are accurate, and assess the quality of your milk to troubleshoot the issue effectively.
How should I store my homemade cheese for optimal freshness?
For hard cheeses, wrap them in parchment paper or cheese paper, while soft cheeses should be placed in airtight containers to prevent drying out during storage. Proper storage is key to maintaining quality and freshness.
Can I make cheese without specialized equipment?
Yes! Basic cheese-making can be accomplished with common kitchen items like pots, thermometers, and colanders. However, investing in quality tools can enhance your results significantly and streamline the cheese-making process.
What is the ideal temperature for aging cheese at home?
Most cheeses age optimally between 50°F to 60°F (10°C to 15°C) with high humidity levels to prevent drying out during the maturation process, ensuring that your cheese develops the desired flavors and textures.
How do I know when my cheese is ready to eat?
Taste testing is the most effective method; evaluate the texture and flavor. Soft cheeses can be enjoyed fresh, while hard cheeses should develop deeper flavors over time, indicating they are ready for consumption.
Is it possible to flavor my cheese during the cheese-making process?
Yes! Incorporating herbs, spices, or even fruits can significantly enhance your cheese. Experimenting with these additions can lead you to discover unique flavor combinations that delight the senses and elevate your cheese-making experience.
What common problems might arise in cheese-making, and how can I resolve them?
Typical challenges include unwanted textures or off-flavors. Closely monitor your techniques, maintain cleanliness throughout the process, and adjust pressing or aging conditions as necessary to achieve the best possible results with your cheese.
Connect with us on Facebook for more cheese-making tips!
The post Make Your Own Cheese at Home: A Simple Beginner’s Guide appeared first on https://cookinggods.com
The Article Make Cheese at Home: A Beginner’s Simple Guide Was Found On https://limitsofstrategy.com
References:
https://limitsofstrategy.com/make-cheese-at-home-a-beginners-simple-guide/